The practice of increasing the visibility and ranking of a website in search engine results pages (SERPs) is referred to as search engine optimization, abbreviated “SEO” for short. I’m an SEO pro, I do this every day and I just wrote this, but I already have a massive 🤯 HEADACHE after reading it once! Ours is an industry full of acronyms and jargon, but I’ll try to keep it simple in this post. SEO and SERPs are just two of the many basic concepts you need to understand before asking questions like ‘what are Dofollow and Nofollow in SEO. We’ll cover it all at a high level below.
Table of Contents
Links get super-complicated and if you need to catch up on your general SEO knowledge before you read this post, just book an audit with our team.
For the rest of you, let’s look at these two HTML link attributes you can add to your website’s content and understand just how they work.
DoFollow Versus NoFollow Links
Building links to your website from other websites is a significant component of search engine optimization (SEO), and I don’t see that changing anytime soon. We’re operating in an environment where GPT3 Chat and other AI-based technology makes content production more of a commodity than ever before. So…if content gets cheaper, my suspicion at the time of writing is that links may be more valuable in the next few future updates to the Google core algorithm. That would be easier to pull off from an engineering standpoint than trying to differentiate between human-edited, quality articles and 100% AI content.
Since links are going to be important to SEO for years to come, you have to understand the difference between a ‘DoFollow’ and a ‘NoFollow’ tag in HTML.
There are two different primary kinds of links that you can create in HTML code: dofollow and nofollow links.
In this article, we will discuss the distinctions between these two different connections, as well as the circumstances where each one is appropriate. I should note that there are two other additional link types – UGC and Sponsored Content – but this article is already turning into boringly nerdy shit, so I’ll try to keep the rest of this post as fun as possible for you and cover those in a future update.
Let’s get started with a basic understanding of links and how they work for SEO.

Understanding Links and SEO
Links connect one page on the Internet to another by allowing readers to click text or an image and go to a new page that expands on the topic they first started reading. The more links your page has, the more traffic you can generally expect from Google and other search engines.
SEO experts know that backlinks are essential for the success of any website.
But what many don’t know is the difference between nofollow versus follow backlinks. Nofollow links supposedly do not pass along SEO value in the form of PageRank, while follow backlinks do help to boost your rankings based on that original patent. PageRank was a revolutionary development that set Google apart from all the other search engines back in the 90s, when those of us old enough to remember were still dialing in on a 56 kbps ☎️ connection.
PageRank still makes up a large portion of the overall core algorithm and the idea that it doesn’t pass through NoFollow links is very contested in SEO circles these days.
In reality, we’ve seen that those Nofollow links are now treated more like a suggestion by Google and they may still pass valuable topical relevance to your pages, which boosts other SEO metrics.
Nofollow links were made especially for blog comments, forum posts and other user-generated content in order to prevent comment spammers from gaining an advantage by flooding websites with useless links. It also makes sure that the search engine does not have to crawl sites that may be low quality or often contain malicious content. On the other hand, ‘Follow’ Backlinks are intended to point to higher-quality sites with valuable content that search engines can review and use as a factor in their search rankings. Since these new link attributes were first introduced many years ago, their meaning and use has evolved. In the meantime, user generated content was given its own category – UGC – and a new tag for Sponsored content was added.
Link attributes in HTML get complicated, but the easiest way to start learning is to understand the classics – DoFollow vs. NoFollow:
What is a Dofollow Link?
A link that “passes along link juice” to the website it is linking to is known as a dofollow link. This implies that the website being linked to will see a slight improvement in search engine positioning thanks to improved PageRank metrics. The most frequent kind of links are dofollow links, which are produced whenever you add a hyperlink to the text on your page without specifically employing the nofollow attribute or any others.

A dofollow link might be one that leads from a blog post on cats to a website about dogs with a page on how they can get along together, for instance. The link from your blog post about cats will help the website regarding dogs in the search engine rankings a little bit, but you didn’t gain commercially from the link and it is extremely beneficial to your readers who want to learn more about related pets.
Followed Links are NOT All Created Equal!
The more authoritative your source is, the better – this means that if your follow backlink comes from an industry leader who has lots of organic traffic, then it will be much more beneficial than a link from a less trusted website or one with very little traffic. These days, we often see Nofollow links from high authority / traffic sites outperforming followed links from sites that don’t have a great SEO strategy in place.
When Should You Use Dofollow Links?
Since dofollow links are the default link type and they help raise your website’s search engine results, you should employ them the majority of the time when you’re actively building links.
There are many circumstances where using dofollow links is advantageous:
- When you want to encourage other websites to link to yours, dofollow links are best.
- When you’re linking out to high-quality websites that are pertinent to your niche in a way that’s not perceived as a commercial link.
What is a Nofollow Link?
A link that doesn’t (typically) pass on link juice is known as a nofollow link. Generally speaking, the linked-to website won’t see an improvement in its search engine positioning. Using the nofollow attribute is simple! An HTML tag is appended to your hyperlink like in the example below and then the nofollow tag gets seen by search engine spiders that visit that page.

Use the nofollow feature if you want to link to a website about dogs from a blog article on cats, and you’re set up to earn a commission from the dog site. This clearly states to Google that the link is commercial and puts the ball back in their court to decide how they want to treat the link in their algorithm.
A nofollow link’s HTML might appear as follows:
Link text: <a href=”http://www.example.com” rel=”nofollow”>http://www.example.com</a>
When Should You Use Nofollow Links?
In the following cases, nofollow links should be used:
- If you link to a website that sells a product or service you earn commissions on.
- If you’re running an advertising campaign on your pages that includes paid links to other websites.
What happens if I Nofollow internal links?
Noooo! Never do that!
When you add a rel=nofollow attribute to an internal link, you are essentially telling search engines not to follow this particular link. In other words, it won’t count as an inbound backlink for the target page or properly distribute link equity between your pages. This means that the target page won’t get many of the SEO benefits from the link—no extra authority, PageRank, or indexing speed—which would normally result from adding an internal link.
In addition, when search engines crawl your website they use internal links to determine which pages are important (and which ones are not). If you add a nofollow attribute to all of your most important pages, then search engines will assume those pages aren’t as important and won’t rank them as highly in their results. This can be very detrimental for your SEO efforts and should be avoided whenever possible. As a general rule of thumb, I never allow any of my internal links to have a nofollow tag. If I don’t want a particular page to show up in the SERPs, our team applies a noindex tag to that particular page in an effort to save our crawl budgets for more important content.
To ensure maximum benefits from SEO-friendly internal linking strategies, make sure that all of your most important pages are linked internally without any rel=nofollow attributes attached so that search engine crawlers can easily find them and rank them higher in the SERPs!
Sometimes you may have these tags and not even be aware of it because of some setting or glitch in your Content Management System (CMS), so it’s super-important for the success of your business that you go ahead and book that audit so our team can uncover any issues for you.
Do Nofollow links help SEO?
When it comes to SEO, the answer to whether nofollow links help or not is complicated. On one hand, these links are known to not pass along any SEO value in terms of PageRank, so making a link nofollow may not directly improve your rankings. However, there are still multiple benefits of using nofollow links that can indirectly lead to better rankings.
For one thing, it doesn’t look natural if ALL your links are followed, so adding a few nofollow links can make your overall backlink profile cleaner and help you avoid any filters that would otherwise keep your site out of the top search results. Another thing to really keep in mind is that some sites just nofollow all of their external links for whatever reason and if Google values those sites, the links will probably work for you no matter what tag is applied to them.
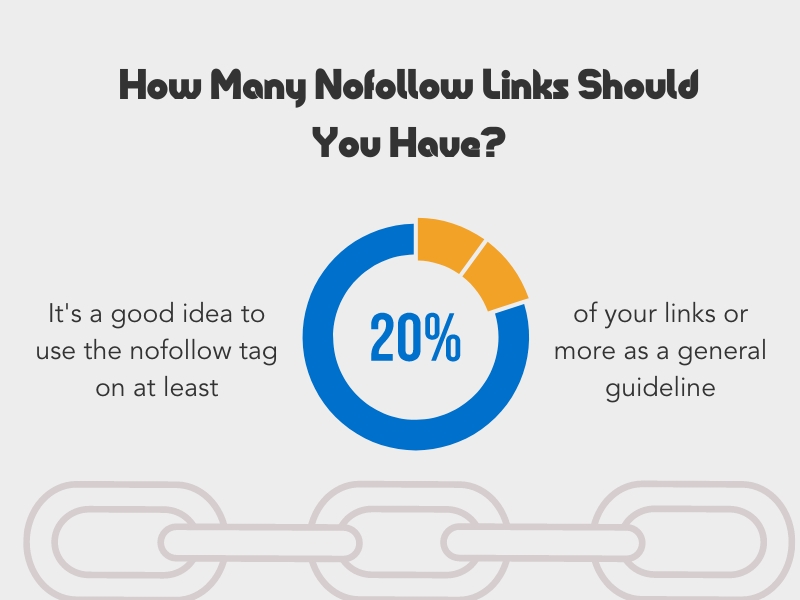
How Many Nofollow Links Should You Have?
Although there isn’t a perfect ratio of dofollow to nofollow links, it’s a good idea to use the nofollow tag on at least 20% of your links or more as a general guideline. The ideal SEO strategy is to explore your niche and see what the average ratio is for sites already doing well in Google.
Balancing your link type and anchor text ratios like this will help you avoid being a victim of a link scam or receiving a Google penalty for having too many dofollow links. Negative SEO is rare these days, but one tactic that may still work for unethical actors is to flood a legitimate site with low quality dofollow links that have overoptimized anchor text ratios. Having a diverse blend of tags applied to quality backlinks can help mitigate these risks to your website.
Understanding the distinction between dofollow and nofollow links is crucial if you want to develop a successful link-building strategy, as link acquisition is a major component of successful SEO plans. No matter what tag is applied to a link, Google’s algorithm will usually make a determination on link value based on multiple factors, and may not always see a nofollow tag as anything more than a suggestion.
When nofollow links come from high-traffic authority sites, they almost always pass at least some SEO value, especially if the content on the page is relevant to the linked resource. All-in-all, PageRank and topical relevancy are probably the two most important factors when it comes to the value of a link, and the weight assigned to each factor by Google may change over time. Tags like follow, sponsored, UGC and nofollow are suggestions the algorithm may or may not follow 100% of the time, so quality links from authoritative sites on pages with relevant content will almost always produce SEO gains no, matter what tags get applied to them.
In general, don’t worry too much about these tags when you’re doing research or outreach. Your focus should be on quality and helping the users of both web pages to find the answers they’re looking for when they click on a link.